The 11 Most Common IT Processes Automated with RPA
IT (Information Technology) departments have traditionally been early adopters of RPA (robotic process automation). The reason is logical. IT have a myriad of processes that are excellent RPA candidates.
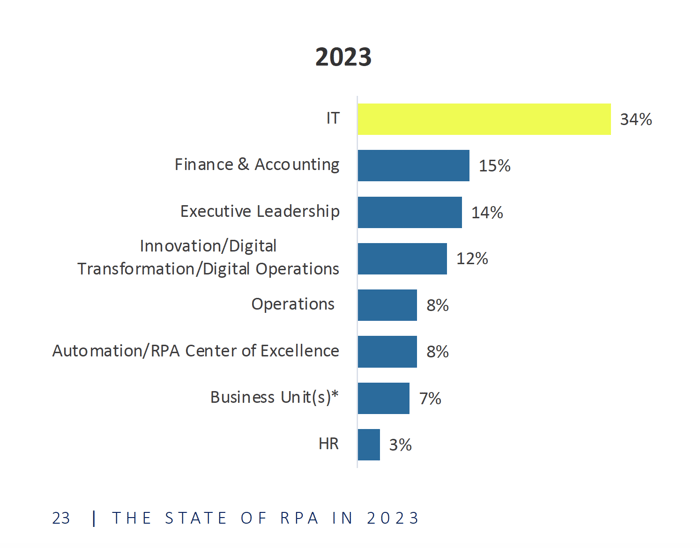
There are countless IT processes that can be automated to optimize quality, speed of execution, and drastically reduce errors introduced through human intervention. In fact, according to Blueprint’s State of RPA in 2023 research report, IT is the most common budget holder and owner of RPA at their respective organizations.
Regardless of where you are in your RPA journey, it’s always beneficial to see what common IT processes others are automating and where they have succeeded. Whether you’re an IT leader who manages your organization’s automation practice or an RPA Center of Excellence team member, here are the 11 most common IT processes being automated with RPA.
Common IT Processes Automated with RPA
1. Data Entry and Migration: RPA has routinely been used by IT to automate the process of entering data into systems, databases, or spreadsheets. This includes migrating data from one system to another, often necessary during system upgrades or integration.
2. Email Processing: Automation has also been employed to sort and respond to routine swivel-chair emails, which can include customer queries, internal communications, or automated alert responses.
3. User Account Management: User management is ripe with automation opportunities due to the rule-based, mechanical nature of these types of tasks. RPA is used to automate the creation, modification, or deletion of user accounts and permissions in various IT systems. This is particularly beneficial in large organizations with numerous employees and frequent personnel changes.
4. Software Installation and Updates: Robotic process automation is increasingly applied to streamline installing or updating software across multiple machines, ensuring consistency and saving time.
5. System Monitoring and Reporting: The perception of RPA is that it’s normally employed to simply execute tasks, but that is a limited understanding of what’s possible. Automations are also designed and deployed to monitor systems for performance issues, security threats, or failures, generating reports and alerts for IT team members where needed.
6. Backup and Restoration: A typical application of RPA in the IT industry is backup storage management. Automations are designed to manage regular backups of critical data and facilitate quick restoration in case of data loss or corruption.
7. Network Monitoring: IT teams also use RPA to monitor network performance and alert the appropriate personnel of issues or outages, improving response times. In these cases, automations orchestrated through RPA tools can monitor network performance, manage bandwidth, and troubleshoot connectivity issues automatically.
8. Report Generation: Regardless of department, report generation is a common use case for RPA. In terms of IT reports, a wide range of regular reports are generated through RPA that include but aren’t limited to analytics on system performance, security, or user activity. Part of the automation is also responsible for distributing these reports to the relevant stakeholders and personnel.
9. IT Service Desk Operations: RPA is commonly used to automate routine service desk requests like password resets, printer configurations, or basic troubleshooting. It’s also used to automate initial responses to help desk inquiries, ticket categorization, and routing to the corresponding team member so it can be prioritized and addressed.
10. Compliance Monitoring and Reporting: One of automation’s biggest benefits is its efforts to fortify regulatory compliance. IT teams create automations that ensure systems and processes comply with internal policies and external regulations. Bots are also designed and deployed to generate the necessary documentation for audit trails.
11. Patch Management: Applying patches is a common procedure for all IT departments. RPA has commonly been deployed to automate the process of applying patches to software and systems, a measure that is crucial for security and performance.
Conclusion
Discovering what other IT teams have automated to maximize RPA returns and realize exponential ROI in terms of better performance and quality is always helpful.
IT has been an ideal starting point for RPA because of the technical complexity of this technology that demands highly skilled employees to implement and manage it; however, the nature of IT tasks also make it the perfect fit. IT is overrun with a number of routine, swivel-chair tasks that can be automated with RPA to improve speed, performance, quality, and most importantly, enable IT professionals to focus on more engaging, mission-critical projects.
Share this
Recent Stories

The Size of RPA Toolchains in 2023

Why Workflow Automation Projects Fail (and How to Get Them Back on Track)