How Will Artificial Intelligence (AI) Change Automation?
Chat-GPT and GPT-4’s booming popularity and widespread application dominated headlines in the early part of 2023. For a while, professional media outlets and networks like LinkedIn were flooded with stories of how artificial intelligence (AI) was here to stay and would forever change the nature of work as we know it.
Accessible and free large language models (LLM) and generative AI with various applications is certainly newsworthy. However, for those deeply entrenched in the automation space, AI is nothing new. For quite some time, thought leaders have been discussing and predicting the wide-scale implementation and application of intelligent automation.
The narrative around the coverage behind Chat-GPT and GPT-4 was dominated by how it was going to transform modern work and more cynically, eliminate jobs. The ongoing writers and SAG (Screen Actors Guild) strike that’s brought Hollywood to a halt is a testament to that perception.
The narrative around RPA at the peak of its hype cycle was that it would also eliminate jobs. That led to experts spending a lot of effort quelling sensational perspectives with the reality that automation would simply augment work by removing mundane, mechanical business tasks and enabling employees to focus on more business-critical and engaging work.
The same can be said about the latest AI craze making waves. Human supervision and intervention are still crucial and necessary. Just like intelligent automation, generic AI simply isn’t ready for prime time, but that doesn’t mean companies shouldn’t embrace it now and prepare themselves for all the benefits it has to offer in the future. In that spirit, this article provides an overview of how artificial intelligence (AI) and intelligent automation will change automation moving forward.
What is Intelligent Automation?
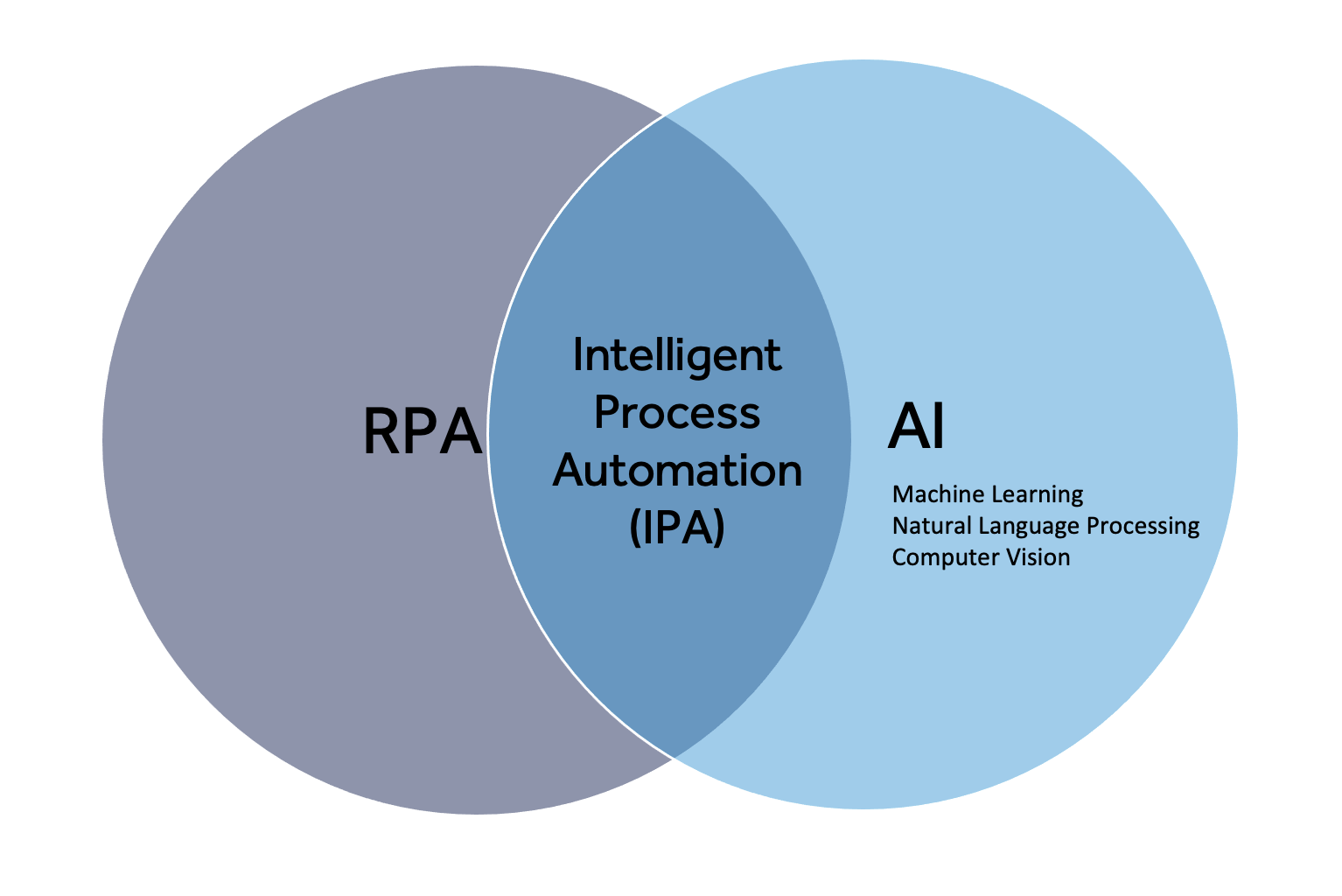
As we’ve explained before in this blog, intelligent automation is the application of different technologies to automate more complete, end-to-end business processes. RPA (robotic process automation) is combined with artificial intelligence like machine learning (ML) and natural language processing (NLP) to automate more complex business processes.
How Artificial Intelligence (AI) Will Change Automation
Automation will move beyond task automation and onto end-to-end business process automation
At the moment, the automation programs organizations have adopted and implemented focus predominantly on RPA. RPA is the automation of simple, rule-based business tasks. A good example of a business task that is automated with RPA is extracting the amount from an invoice in an email and inputting it into an ERP (enterprise resource planning) like SAP.
The application of AI technologies with cognitive capabilities like machine learning, computer vision, and natural language processing will enable intelligent automation to automate complete and complex decision-based business processes.
Automated processes will be able to better understand and process unstructured data, make decisions, and learn from patterns. Automation will become much more sophisticated and therefore exponentially increase the efficiency gains and returns companies have already realized from RPA.
Enhanced automation candidate identification
Identifying RPA candidates for automation predominantly relies on manual analysis and assessment with the use of checklists in some cases. Another source of identifying business tasks for automation are requests brought forward by different departments or business units.
Many organizations have also adopted technology to help with the endeavour of uncovering tasks to automate. Process and task mining tools are being implemented and have produced positive results even though they come with their own challenges like the difficulty of sifting through massive amounts of data to make sense of what’s been extracted.
With AI rapidly evolving, it is being applied to process and task mining technologies. The result will be that a more sophisticated application of AI in technology like process and task mining will enable these solutions to analyze larger amounts of data, intelligently identify patterns, pinpoint bottlenecks, and become much more effective and efficient at discovering automation opportunities for accelerated scale and greater ROI.
Enhanced automated chatbots
Integrating sophisticated chatbots using low-code solutions like Microsoft’s Power Virtual Agents (which makes up part of the Power Platform) is in full swing. Currently, they can successfully and efficiently handle routine customer service requests.
The continued application of AI—as it becomes more stable and robust—in those chatbot apps will deliver much more intelligent chatbots that are capable of handling complex requests with the addition of natural language processing and other cognitive capabilities. The result will be increased efficiency and better customer experiences; two of the premier objectives of automation.
Improved data extraction
RPA is limited to structured data inputs. As AI integration grows in the realm of automation, data inputs will expand to unstructured sources like email, documents, and images with AI technology like computer vision.
The by-product will be increased data processing and analysis, expanding automation beyond its limitations today for even more efficiency and speed.
Conclusion
Artificial intelligence has already started to skew the boundaries of automation. The integration of AI technologies like machine learning, natural language processing, and computer vision are rapidly being added to automation solutions delivering intelligent automation in place of traditional RPA.
While intelligent automation is still some ways away from mass-scale implementation, the adoption curve is starting its steep ascent as organizations start to embrace the innovations rapidly being deployed for more sophisticated and efficient automation that transcends RPA.
Share this
Recent Stories

What is Intelligent Process Automation (IPA)? All You Need to Know

Intelligent Automation Solutions for Enterprise Processes